26 Rare Facts about the USSR
For decades, the USSR was a behemoth force to be reckoned with in terms of global politics and warfare. Starting with the Bolshevik revolution, the rise of the Soviet Union took place across Russia and Europe’s Eastern bloc over what almost amounted to a century. During this time, some of the most shocking political events took place – along with it, a number of human tragedies, and devastations such as the Chernobyl power station disaster.
Did you know that the USSR finally embraced one of the US’ biggest and best-loved brands by the 1990s? Maybe you’re unsure of just how much space the Soviet Union actually took up. In any case, make sure to dip into our complete fact file on this extraordinary period in Russian history.
1. What does USSR mean?
The letters USSR stand for ‘Union Soviet Social Republic’.
2. Soviet itself is an interesting word.
The word ‘Soviet’ in itself means ‘council’.
3. The Bolsheviks started chaos.
In 1917, the Russian Provincial Government was overthrown by the ‘Bolsheviks’.
The Bolshevik legion was a ‘far left’ political party, founded by Alexander Bolkanov and Vladimir Lenin.
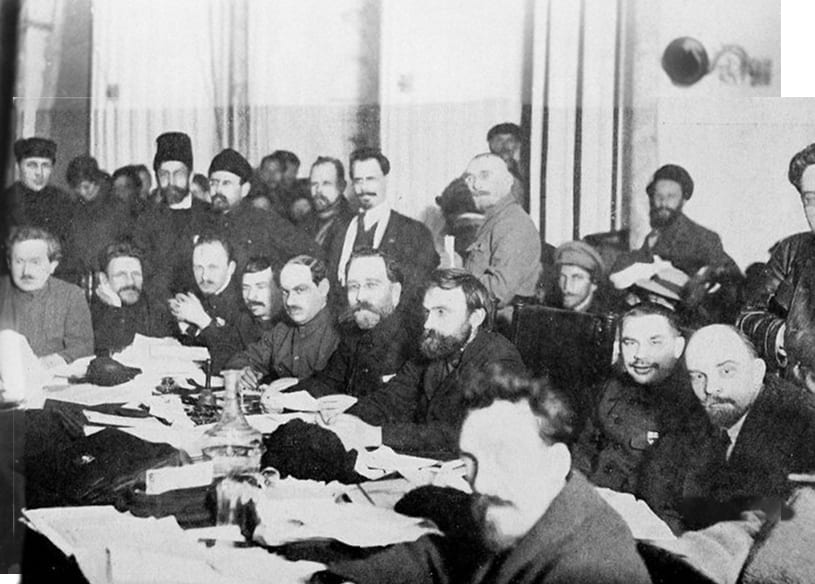

Bolshevik Party meeting
4. What was Eurasia?
Multiple independent republics were geographically aligned but governed separately, until 1922. The region was collectively known as part of ‘Eurasia’.
However, the USSR was founded in 1922, and this is when things changed.
5. Lenin rose to power in 1922.
Vladimir Lenin became leader of the newly formed Communist Party and at the same time, in 1922, Lenin took control of the Government.
6. Russia brought in many territories to help.
By way of a treaty, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Transcaucasia, and the Ukraine joined Russia to form the USSR.
During the years of its existence, other states joined the USSR, allowing it to swell geographically, and its power continue to build.
7. By the 40s, the USSR was a huge deal.
In 1945, the USSR was officially ranked as a ‘super power’, in company with the USA. The two countries were, of course, allies in the Second World War.
8. The USSR’s name changed somewhat.
Over time, the USSR also became known as simply the ‘Soviet Union’.
9. Marxism was a big deal for the USSR.
The USSR is noted to be the first country in the world to have been run and based entirely on Marxist Socialism.
Defined as ‘working for the collective good’, Marxism, as a political and economic theory, had no room for differing social classes. Everyone was meant to be considered equal, in theory to eliminate social unrest based on status.
The theory of ‘Marxism’ was the brainchild of Karl Marx.

Soviet and American troops
10. Lenin really wanted Marxism to work.
The aim of Lenin, with the theory of the ideals of Marxism, was for the capitalist state to be replaced by a single-party, communist state. This was to be governed by a ‘dictatorship’ overseeing the ‘proletariat’ (workers).
11. Lenin took charge for a short time.
Lenin was in the role of Chairman of the Council of Commissars of the Soviet Union from December 30th, 1922 until his death in 1924.
12. He died at a young age.
Lenin died as a result of three strokes which followed in quick succession after he had been shot twice. He was only 53 when he died.

Lenin in 1919
13. Stalin succeeded Lenin.
Joseph Stalin took over from Lenin as Leader of the Soviet Union in 1924. Stalin then became ‘Dictator’ of the USSR in 1925.
Subsequently, he became Minister for Defense from 1941 to 1947 and was Chairman of the Defense Committee during World War Two.
14. Malenkov didn’t last long.
A short term as Leader of the USSR was Georgy Malenkov, who was only in the role for six months.
15. Khrushchev was in charge for 11 years, however.
Nikita Khrushchev took over as Leader of the Soviet Union from September 14th, 1953 to October 14th, 1964.
Khrushchev’s policies included ‘anti-Stalinism’ and ‘anti-religion’ campaigns. He would later resign from the leadership as a result of poor health.
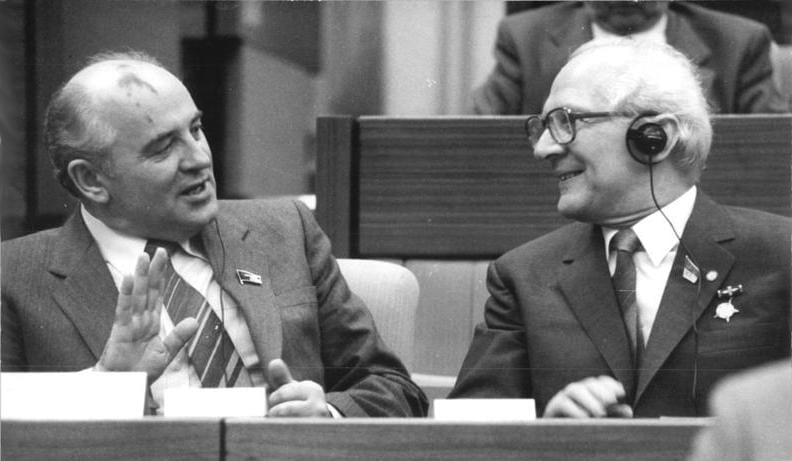

Gorbachev with Erich Honecker
16. Gorbachev wanted to bring about serious changes in the 80s.
In the 1980, Mikhail Gorbachev was General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. Gorbachev wanted to streamline the government bureaucracy and improve the economy.
Gorbachev is credited with making two important major changes. One of them was a sense of ‘Glasnost’, meaning ‘openness’, and ‘perestroika’, meaning ‘re-structuring’.
17. Many were unhappy with Gorbachev.
The result of Gorbachev’s practice of openness and restructuring led to a massive uprising of discontent. The media world let loose with information and opinion levels previously unheard of.
18. However, opinion remains divided.
It is widely accepted that Gorbachev’s actions brought about the demise of the Soviet Union. People were divided on his decisions.
Some felt he was a pioneer who released social constraints and created freedoms for cultural policies.
Others were less comfortable with Gorbachev’s notion of sudden revolutionary change and were wary of what the prospects may be.
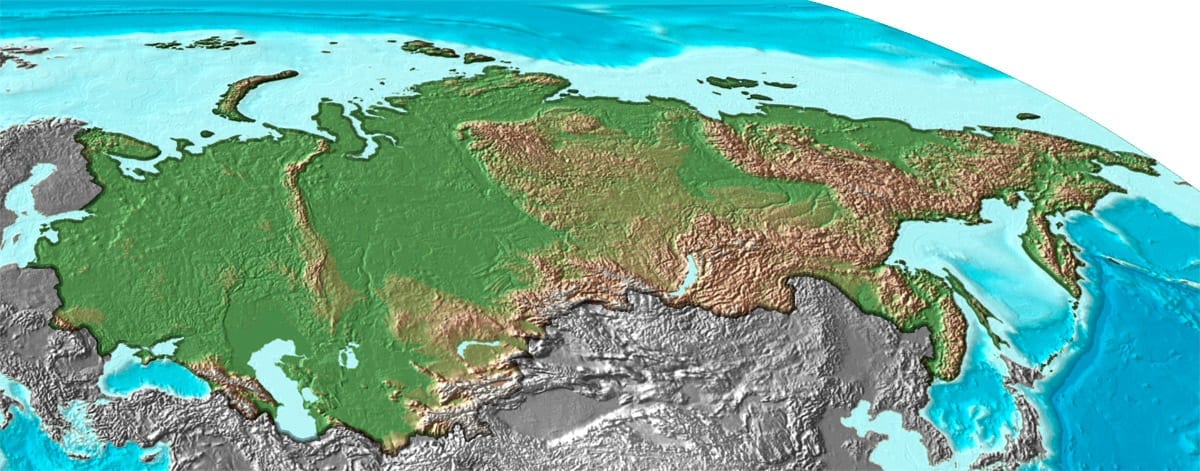
Map of the Soviet Union
19. The USSR was massive by the 90s.
By January 1991, the Soviet Union was the largest country in the world. It last measured 8,650,00 square miles.
The land covered by the Soviet Union was just less than one sixth of the total area of land in the world!
The Soviet Union had a population of over 290,000,000 in 1991.
20. They had huge nuclear arsenals.
The Soviet Union had boasted of storing ‘thousands of nuclear missiles’ and the Media, spreading this boast, raised both awareness and fear of their military strength.
21. The Union catered to many groups of people.
Over 100 different Nationalities lived within the boundaries of the Soviet Union.

The DniproHES hydro-electric power plant, one of the symbols of Soviet economic power
22. Business was booming.
The Soviet Union economy was recorded as ‘being the second largest in the world’ in 1990.
23. But what about the Black Market?
It is known that the Soviet Union had within it a broad and successful ‘Black Market’. This rose to prominence when oil prices dropped significantly, and political unrest caused restraint with economic development.
24. The Soviet Union kicked off the 90s with a burger bar.
On January 1st, 1990, McDonalds opened its first chain in Moscow.

25. Chernobyl devastated the Union.
On April 6th, 1986, a catastrophe befell Chernobyl power station. Whilst Gorbachev actively guarded military strength for the possibility of nuclear war, no one foresaw the utter devastation a Russian missile would cause its own people.
The accident at the Nuclear Power Plant in Chernobyl was both a tragedy and an embarrassment. Gorbachev later made a famous and poignant recording saying later that ‘Even more than my launch of ‘perestroika’, Chernobyl was perhaps the real cause of the collapse of the Soviet Union’.
26. The USSR split up by 1991.
The demise of the USSR took place in 1991. Since then, member states have split off into their own countries, and the Russian Federation has taken the place of its main base.

Chernobyl
FAQs about The USSR
What is the USSR called now?
The USSR actually split into many different territories, though the main part of Russia is now called the Russian Federation.
What was Russia before the USSR?
Russia was originally known as the Empire of The Tsars before the USSR came into force.
What led to the fall of the USSR?
It’s thought that continuing democratization, largely on the part of Gorbachev, led to the dismantling of communism and the USSR.
Do you know any interesting facts about the USSR? Share them in the comments below!
This page was last modified on January 1, 2024. Suggest an edit